A 148-home central Florida development may be the sign that net zero living has gone mainstream.
View the original article here.
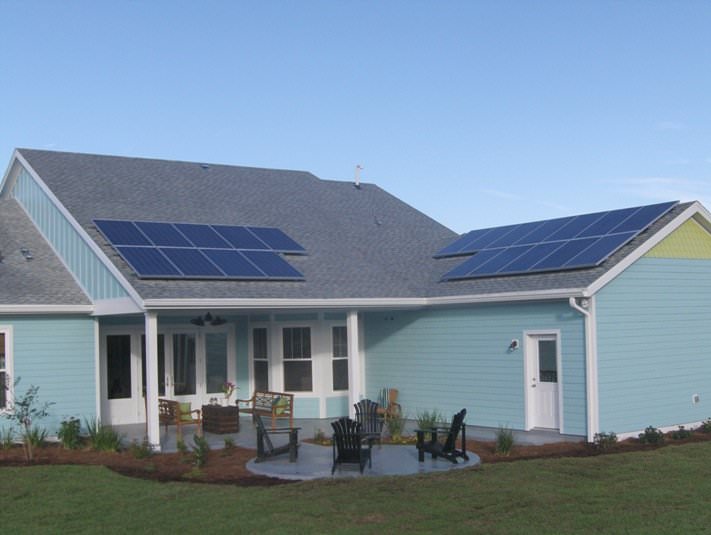
Long-time builders Greg and Sue Thomas have opened Green Key Village, a 78-acre net-zero home development in Lady Lake, Florida, about 50 miles northwest of Orlando. The homes will be certified under the Florida Green Building Coalition, and one model home has already achieved a platinum rating, Thomas said. The homes will also be Energy Star and Department of Energy Zero Energy Ready Home. Each home will be HERS rated, and the goal is to achieve a HERS index of 50-55 prior to renewable energy installation. An average code built home has a HERS Index of 100.
Also, the homes have earned the Florida Friendly Landscaping silver designation in recognition of resource-efficient landscape design.
To help them with the challenge of selling a net-zero community, the Thomas’s brought on Tony Richardson to help them sell. With more than 30 years of experience in green home building and marketing, Richardson is a Green Designee of the National Association of Realtors, and a USGBC Green Associate.
Green Key Village is the first residential neighborhood in the nation designed using software offered by Ekotrope that was developed at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. The software analyzes 10,000 variables to give designers data to compare each component of the home by its cost and energy efficiency. They can evaluate wall thickness, window size, insulation depth and every other aspect of the home. The development offers eight floor customizable plans in one- and two-story options. ranging from $318,000 to $414,000 and home sizes ranging from 2,755 square feet to 3,637 square feet.
Thomas said the Ekotrope analysis helped them make cost/benefit trade offs. For example, the home uses a 15-SEER rated air conditioning unit because the payback for a higher rated unit would have been longer than the life of the product. The analysis also showed that with the high-efficiency HVAC and a heat pump hybrid water heater, one of the most efficient on the market, the HVAC heat pump had to be only a 2.5-ton capacity in the 3,000-square-foot model home.
In an exclusive interview with ProudGreenHome.com, Greg and Tony talked about the challenges of presenting high performance, net-zero living to a mass-market real estate environment.
What was your vision for the community?
Greg: Where we live there’s a house with a big front porch and every afternoon the neighbors gather on that porch. In my mind, if all our houses had front porches I think it would be a great gathering place for neighbors to meet and fellowship. We wanted to build that kind of a neighborhood.
My dad was a builder, and I’ve been a builder for 30 years. It’s always been concrete block and stucco. That’s worn out. I said, let’s look for something different. We went to the coast, and saw houses with bright colors with lap siding, a metal roof and big windows covered with Bahamas shutters.
We put it out here in the middle of Lady Lake and have a great looking subdivision that isn’t made from a cookie cutter.
So that was our goal. We wanted to combine old Florida charm and new green living. I think we’ve hit it pretty good.
What are some of the challenges in communicating a high performance home to the general buyer?
Greg: I like to give them a brief overview and then back off until they ask more questions about it. It overloads them; actually, their eyes glass over when they’re just looking for the granite countertops.
It’s hard not to load them up with all the information, but we’ve spent so much money on this technology you hate to not to.
What makes your homes perform so well?
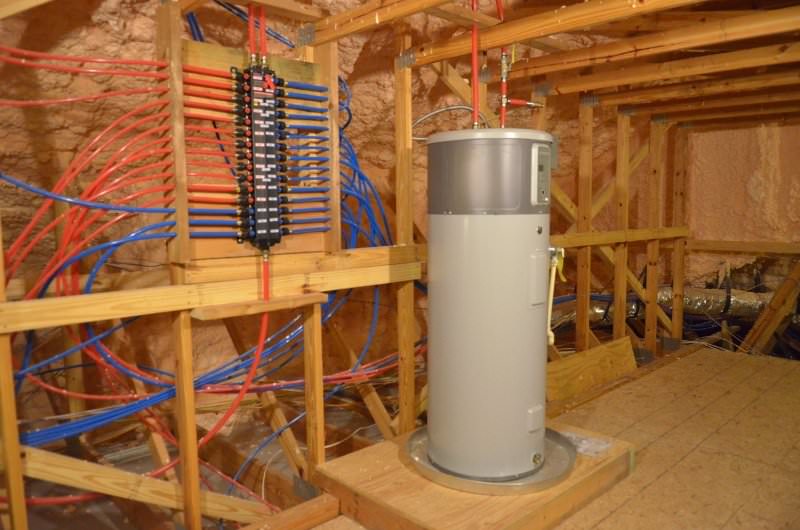
Greg: We used Ekotrope software to optimize the house design and balance all the HVAC loads, insulation and so on. We use open-cell spray foam on the underside of the roof deck, and the mechanical room is in the attic but it’s in conditioned space in the attic under the foam on the roof. Depending on the floor plan, the room can be 200 square feet to 500 square feet.
The GE heat pump water heater is in the room, and with it being a heat pump it keeps that area cooler and drier as it operates. It’s like having a dehumidifier up there. The manifold block plumbing system originates there too, right next to the water heater. And the HVAC ductwork is in there, too. It all works together.
It’s a nice attic room with stair leading to it homeowners could use for storage as well.
What are some of the green aspects of the home?
- Icynene open-cell spray foam insulation
- Advanced framing techniques
- GE heat pump water heater
- Two Panasonic energy recovery ventilators
- Amana 15 SEER heat pump
- Double pain Low-E windows from YKK
- LED & CFL lighting
- Energy Star appliances
- WaterSense fixtures
What is the result of your green building strategies?
We cut the air conditioning load almost in half by going with the open cell spray foam insulation on the walls and ceiling. With the A/C, water heating, lighting and all the appliances are Energy Star rated, we’ve brought down our power usage on this house. Here an average house uses 1,500-1800 kilowatt/hours per month, and we’re down to less than 1,000. Then we take care of that with the solar panels.
What is your water conservation strategy?
As part of the Florida Green Building Coalition certification, we are certified to have less than a half-gallon of water in the lines. We use a maniblock plumbing system and PEX tubing.
Are you using advanced framing techniques, and how does that work with the wind load requirements?
We use regular 2×4 framing and what’s referred to as the “California corner,” two studs in the corners and we use horizontal blocking that gives you a nailing surface. You have to re-train your framers and help them remember that you can’t load up these corners with studs. We’ve heard of people going 24-inch centers but we haven’t gotten brave enough to do that.
All our homes have to be certified to meet 130 mph wind load. We use a solid sheathing with 4×10 OSB that helps fight uplift. Also the tie downs and anchors come into play to meet the wind load regulations.
Is there a price premium on the all the green attributes of the homes, and how do you communicate that to the buyers and the financial community?
From the water heater to the insulation the lighting to bath fans, to the ERV and solar panels, when you add all that up, the difference is $35,000 to $40,000 of additional value to the home.
We have prepared an addendum for our contract, because when you attach an addendum for the contract, the appraiser for the bank has to look at anything attached to the contract. For each model we have addendum that shows our cost for open cell spray foam insulation so and compare that to the traditional batt foam insulation on concrete block.
That also gives the homebuyer the documentation they need to apply for their solar tax credit.
How do buyers respond to the idea of a paying a premium for a high performance home?
We tell them, compared to an average $200 a month power bill, with the lower utility costs of these houses, you have $42,000 to $43,000 more power buying over the life of the mortgage. Whether you’re paying cash or using a mortgage, your overall buying power is that much more.
The math works. And you get a much a much healthier house. With the no-VOC paints, the low-VOC carpets and cabinets, your home is healthier. The ERVs are bringing in fresh air 24 hours a day.
Tony: These homes are priced very comparably to homes of similar size if they they had the same quality as these homes.
We can show on a cash-on-cash basis, they’ll be not spending more money but making money starting the first month and every month thereafter. There’s no flim flam here; it’s the truth.
Photos courtesy Green Key Village LLC.
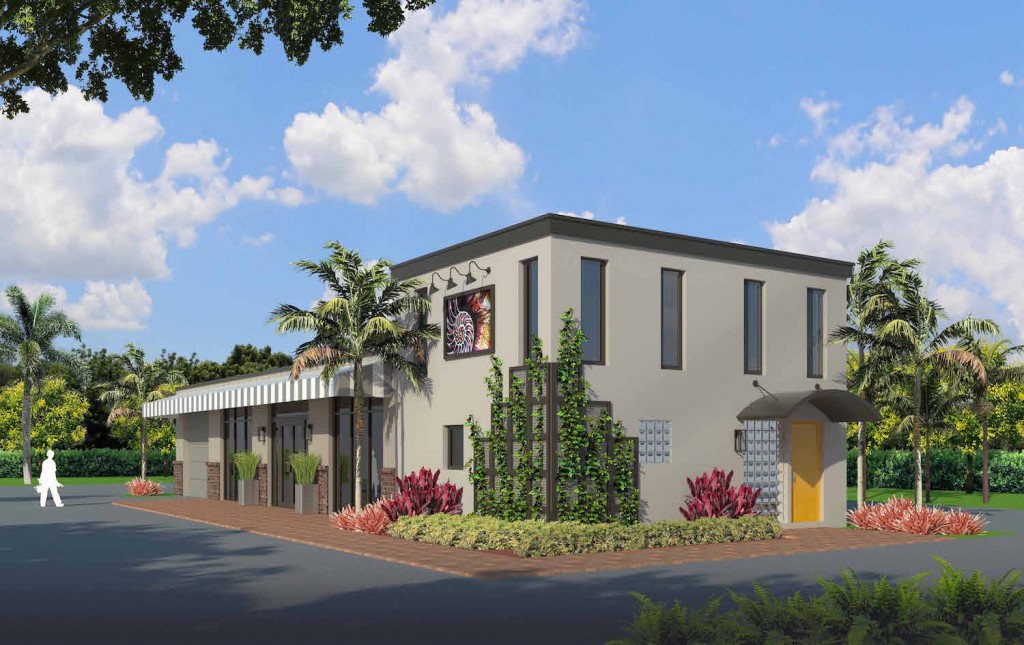



 We are getting close… to completing the build out of the interior of our project. I would like to share some of the design details and finishes that we have chosen. This building is an old auto garage so we are keeping the existing open floor plan of the main garage space with minimum interior walls being constructed. The perimeter concrete walls will remain intact without the addition of a drywall finish. The walls have so much character; the imperfections on the concrete block that have accumulated over the years are too interesting to cover up. The walls will be painted and some of the imperfections enhanced with paint layering. The 3 overhead garage door openings have been replaced with impact windows and doors with the center opening now serving as the main entrance. Since it is important to our design concept to retain as many of the auto garage components as possible we designed this elevation to keep the overhead doors in place behind the new glazing. Manual lift mechanisms have been installed to enable us to raise and lower the garage doors. We are using the roll down doors as large metal shades for both privacy and sun control since the openings are located on the south façade. Broad horizontal stripes will be painted on the interior of the overhead doors to add a bold touch to the space when lowered.
We are getting close… to completing the build out of the interior of our project. I would like to share some of the design details and finishes that we have chosen. This building is an old auto garage so we are keeping the existing open floor plan of the main garage space with minimum interior walls being constructed. The perimeter concrete walls will remain intact without the addition of a drywall finish. The walls have so much character; the imperfections on the concrete block that have accumulated over the years are too interesting to cover up. The walls will be painted and some of the imperfections enhanced with paint layering. The 3 overhead garage door openings have been replaced with impact windows and doors with the center opening now serving as the main entrance. Since it is important to our design concept to retain as many of the auto garage components as possible we designed this elevation to keep the overhead doors in place behind the new glazing. Manual lift mechanisms have been installed to enable us to raise and lower the garage doors. We are using the roll down doors as large metal shades for both privacy and sun control since the openings are located on the south façade. Broad horizontal stripes will be painted on the interior of the overhead doors to add a bold touch to the space when lowered.