This article is republished on Sustainable Benefits for educational purposes.
View the original article here: Perkins+Will’s Ideas + Buildings
By Kate Kerbel
While our industry’s focus on wellness may seem like just the latest trend, occupant health has been an important goal of the built environment for centuries. In the 1800s, urban infrastructure allowing access to fresh water, natural light, and clean air significantly reduced the number of deaths from infectious diseases like tuberculosis, cholera, and yellow fever. Additionally, in the 1900s, doctors consulted on the design of school gymnasiums, advising on how the environment could help support human health.
Today, with individuals spending on average over 40 hours a week at work, health and wellness are taking center stage. Labor and healthcare spending also comprise the bulk of operating expenses—making happy and healthy employees a smart investment.
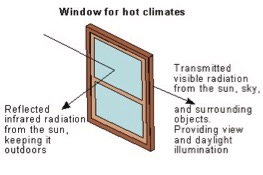
Since its development in the 1990s, the LEED rating system has been applied to over 19.1 billion total commercial square feet. Along with other systems like BREEAM, Energy Star, and the Living Building Challenge, green building design and operations work to conserve energy across the globe. A serendipitous byproduct of green design has become apparent: people like working in green buildings better. Green buildings ensure access to daylight, incorporate biophilia, provide clean air, and leverage healthy materials; it’s no wonder people like spending time in them.
In recent years, two new wellness rating systems have emerged. Both use research-based strategies to evaluate buildings not by how much energy they save or how they impact the environment, but by how they can directly contribute to occupant health.
WELL was developed by Delos and has a somewhat similar framework and documentation process to its “cousin,” LEED. Both certifications are administered by the Green Business Certification (GBCI), which continues to improve and streamline the synergistic documentation processes.
Fitwel, developed by U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the General Services Administration (GSA), and administered by the Center for Active Design, aims to identify the most impactful strategies for space and does not require a technical design background to administer.
Perkins+Will is well versed in both systems. We’ve committed to achieving Fitwel certification for all our North American offices, and we have a handful of WELL-certified projects, including the ASID Headquarters—the first space in the world to earn both both LEED and WELL Platinum Certification.

The ASID Headquarters in Washington, D.C., was WELL Certified at the Platinum level under WELL v1 in June 2017.
As a Fitwel Ambassador and our firm’s first WELL Accredited Professional, I’ve gotten a lot of questions about the two systems. In just one year, I have seen a huge increase in interest, especially from developers. In response, here are my answers to two of the most frequently asked questions from those considering these emergent systems.
HOW DOES WELL DIFFER FROM LEED?
Impact Categories
As opposed to LEED’s Location & Transportation, Sustainable Sites, Water Efficiency, Energy & Atmosphere, Materials & Resources, and Indoor Environmental Quality categories, WELL divvies up its 100 Features (credits) into: Air (Quality), Water (Quality), Nourishment, Light, Fitness, Comfort, and Mind. There are naturally some synergies between the categories: For example, an automated daylight sensor that dims overhead lights when sufficient daylight is present saves energy, but it also reduces glare and allows people to work in a naturally lit space. Conversely, some of the categories prioritize occupant health over energy savings . For example, WELL requires that paper towels be provided in restrooms because automated hand blowers are less sanitary. Through the LEED lens, the additional use of material would be discouraged.
On-Site Testing
LEED requires thorough documentation for the majority of credits, including annotated floor plans, measurements, manufacturer documentation, etc. WELL, on the other hand, requires signed letters of assurance from the architect, contractor, MEP engineer, or owner for many Features. Then, the GBCI sends their own WELL Assessor to the site to visually observe that all the policies are in place, and to conduct rigorous testing to confirm air and water quality standards.
Recertification
Unlike LEED, WELL requires project recertification for construction/major renovation projects as well as interiors projects every three years, which means a WELL Assessor will come back to the site to make observations and rerun quality tests. Projects may either meet the same level of certification they originally earned, be awarded a higher certification than their original level, or lose certification. Core and shell projects, however, do not need to be recertified.
Preconditions
There are more preconditions in WELL (called prerequisites in LEED) than you might expect. For certification or compliance to be awarded, all applicable WELL preconditions need to be met. The number of preconditions that must be met depends on the project typology. For example, new construction/major renovation projects have 41 preconditions, while core and shell projects have 26.
Levels of Certification
Certification starts at silver and consists of Silver, Gold, and Platinum. Meeting all of the preconditions earns a silver certification. Gold level certification is achieved by meeting all WELL preconditions, in addition to between 40 to 80 percent of the optimization features. Platinum level certification is achieved by meeting all preconditions, as well as 80 percent or more of the optimization features.
WHICH STANDARD IS BEST FOR MY BUILDING?
There are several compelling reasons to use each system. For instance, if a client comes to us with a large real estate portfolio and is interested in tracking hundreds of locations, Fitwel would be the best choice. Fitwel is relatively quick and straightforward for facility managers to use themselves to find out if their buildings earn zero, one, two, or three stars. Furthermore, with a large portfolio, facility managers would be able to benchmark all of their locations and set company goals. For example, they may want to bring all of their locations up to two stars over a certain number of years. Fitwel gives the user feedback regarding what changes the building/operations can make that will have the most impact on improving their workplace.
WELL, because of the more substantial effort and cost, realistically would be ideal for a few featured locations of a large portfolio at this point in time. The process of achieving WELL looks similar to that of achieving LEED: It should be discussed early in the project design process and will require members of the architecture, engineering, and operations team to work together to submit documentation.
Lastly, a client could also pursue both Fitwel and WELL for a building, as we are doing with our own Perkins+Will Dallas office, since there are unique benefits to both. Also, keep in mind that certifications are not necessary to ensure the design of a healthy space. Similar to designing green buildings, it is completely possible to design the healthiest of spaces using thoughtful design concepts that great architects have pursued throughout history without completing a formal documentation system.