 by Paul L. Jones, CPA & LEED Green Associate
by Paul L. Jones, CPA & LEED Green Associate
 In our February issue of Sustainable Benefits, Kendall Gillen introduced the concept of a Circular Economy (see “The Changing Face of Waste Management and the Shift Toward a Circular Economy“) by contrasting it with “today’s linear consumerist society. Once a material of substance is no longer considered useful, it is discarded and left in the hands of waste management….”
In our February issue of Sustainable Benefits, Kendall Gillen introduced the concept of a Circular Economy (see “The Changing Face of Waste Management and the Shift Toward a Circular Economy“) by contrasting it with “today’s linear consumerist society. Once a material of substance is no longer considered useful, it is discarded and left in the hands of waste management….”
“Circular Economy” is defined as “a generic term for an industrial economy that is producing no waste or pollution, by design or intention, and in which material flows are of two types: biological nutrients, designed to reenter the biosphere safely and technical nutrients, which are designed to circulate at high quality in the production system without entering the biosphere as well as being restorative and regenerative by design.” (Wikipedia)
In its report published in July 2014, “Growing a circular economy: Ending the throwaway society,” Great Britain’s House of Commons Environmental Audit Committee says, “The current way our economy consumes resources is not sustainable. A ‘linear approach – where materials are extracted, made into a product, used and discarded – wastes valuable resources and damages the environment. In addition, increasing levels of consumption in developing countries will put ever more pressure on the prices of materials and subsequent costs for businesses and consumers. A ‘circular’ approach of re-using resources, maximizing their value over time, makes environmental and economic sense. There are potentially billions of pounds (or dollars) of benefits for businesses across the economy by becoming more resource efficient.”
An early concept introduced way back in September 2009 was the circular nature of sustainability as practiced in society represented by the Ricoh Cornet Circle reproduced below.
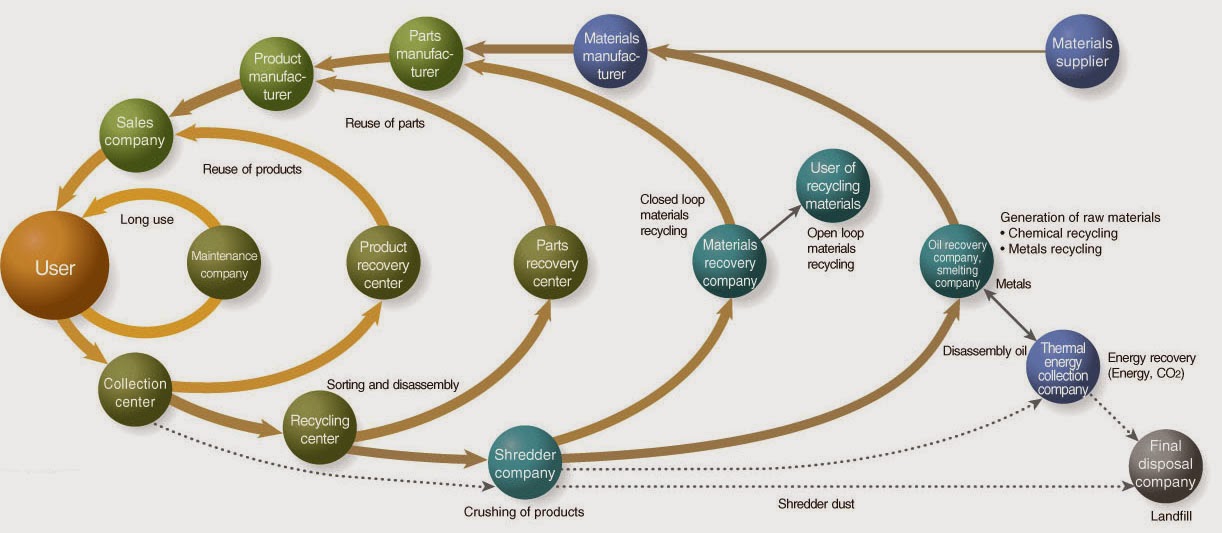
In a 2015 report, Jennifer Gerholdt, environmental program director of the US Chamber of Commerce Foundation, wrote: “If we continue with the business-as-usual approach, companies and society will witness a probable surge in price volatility, inflation of key commodities, and an overall decline — and in some cases, depletion — of critical material inputs.” In fact, according to the World Economic Forum, commodity prices rose more than 150 percent between 2002 and 2010.
In her June 23rd article, “The Evolving Ton and the Circular Economy, “Elizabeth Comere, Director of Environmental and Government Affairs for Tetra Pak, reports: “At the Sustainability in Packaging Conference held in Chicago this past April, a surprising number of presentations focused on packaging recycling topics. Increasing consumer access to recycling, changing recycling behavior through labeling and better linking brand owners with recyclers were among the topics covered. Five years ago, recycling took a backseat to topics such as sustainable design and life cycle analysis. A primary reason for this shift in emphasis is the growing realization of the importance of having an effective post-consumer materials recovery and recycling system, and secondly, concern over the fact that the current system in the United States is falling short of meeting this objective.”
Many companies, including Google and Dell, are already implementing a circular economy model. They are partnering with the Ellen MacArthur Foundation on closed-loop initiatives. These firms see the circular economy not only as a way to reduce waste and improve sustainability performance, but also increase competitiveness, new product development and overall sales. Between January 2014 and August 2015, Dell used more than 4,500 metric tons of post-consumer recycled plastics in its products. Cumulatively, the company has used closed-loop recycled-content plastic across 34 products globally through its closed-loop supply chain, turning waste into a resource.
Analysts have showed that there is considerable financial opportunity, as well as environmental benefit, associated with a scaled-up circular economy. In particular, in the electronics sector, precious metals recovery represents a significant business opportunity. Trucost estimates that if recovery of gold, silver and platinum increased from current rates to 100 percent, the financial and natural capital benefits would increase by $10 billion.
“A shift from a linear to a circular economy could unlock an estimated $4.5 trillion in additional economic growth by 2030,” Gerholdt is quoted by Environmental Leader in an article by Jessica Lyons Hardcastle published 11/19/2016. “The circular economy has captured the imagination of many companies that see the economic innovation opportunities of this more restorative model to tackle sustainability challenges, drive performance, competitiveness and innovation, and stimulate economic growth and development.”
When it comes to burnishing your organization’s or your building’s brand and cleaning its footprint, the efforts center on reducing, reusing and recycling nearly every material used – regardless of whether it is in production, operations or management According to Dan Gilbert, Head of global sustainability for international facilities management company, ISS, the ultimate aim, is to create “zero waste,” which can mean eliminating anywhere from 90% to 100% of the waste your company is putting into landfills. The last 10%, he emphasized, is where the real work is. To get there, organizations need to measure and manage their waste streams, and report their progress at least on a quarterly basis.
“What is the cost of recycling versus putting it in the trash,” Gilbert tells us; “If you save money, your corporate leadership is more likely to get behind the initiative.” For commercial real estate, your tenants will recognize it and value efforts to achieve zero waste.
While many sustainability efforts do require an upfront investment in time and resources, they build a positive community image as well as among potential tenants. Some examples include:
Computers would be the worst thing to toss in the landfill, says Gilbert. That’s because they have an “encyclopedia of metals” that can leach into the ground water system.
Other things that businesses can recycle include office supplies, office equipment, boxes, shelving and racks. Furthermore, cement, asphalt, wood, carpet, pellets and drywall can be recycled or reused.
The companies that accept those items might pay the corporate donor for the materials that will ultimately go into new products. If a mobile phone is built from recycled parts, it prevented waste from going into the landfill and it has created a perfectly good use of still viable parts. Similarly, recycling LCD screens, computer and medical equipment would have the additional benefit of preserving significant amounts of raw materials, such as Gallium in LCS screens and integrated circuits, Beryllium, Niobium and Helium in medical equipment and increasing the affordability of new medical equipment.
Buildings with in-house cafeterias can compost their food waste rather than ditch it in the trash. “Food waste is heavy and it breaks down and creates methane,” says Gilbert. Instead, it can be composted and that enriches the soil. Things like plastic scraps, tableware and coffee cups can also be eco-friendly — meaning they are biodegradable and can be turned into compost.
- Reported today by Environmental Leader. “Dozens of major companies including ABC Disney, Whole Foods and Anheuser-Busch with offices in New York City have diverted at least half of their waste from landfills and incineration, responding to Mary Bill de Blasio’s Zero Waste by 2030 challenge. The 31 business participants collectively diverted 36,910 tons of waste by increasing recycling, composting more than 24,500 tons of organic material and donating 322 tons of food, according to the mayor’s officer”
Every building owner and every business can take steps to be more environmentally friendly. One of the quickest ways to do so is to create separate bins for the recyclables and the real trash — but not to mix the two. Doing so, says Gilbert, could taint the bottles, plastics and papers. And a “single-stream” deposit in which everything goes into one bin is better than having different ones for different items.
As for the businesses that have to invest in the bins: “It’s hard enough to get them to buy one, much less four or five of them,” says Gilbert. A central place to put all recyclables is therefore the best solution. Having trouble finding a vendor to pick up such items? Start with the company that picks your trash, Gilbert said. And if that doesn’t work, get on line and look for one.
He points to a Utah State University audit that found 20-40 percent of the stuff that goes into the trash could be recycled.
The Ellen MacArthur Foundation says the circular economy concept is gaining traction in the US because of the opportunities it offers businesses willing to capture new value from existing operations and resources, for example by redesigning products and business models, building new relationships with customers, harnessing technology to increase the utilization of assets, and switching to renewable energy.
Given the 7.4 Billion people who now roam this earth and the fact that our natural resources are not unlimited, The linear “take, make, dispose” model is not sustainable. We can no longer afford to throw away materials that can be re-used or recycled.
According to Nichola Mundy, senior consultant at Axion Consulting, “The circular economy aims to develop closed-loop business systems that enables economic growth whilst decoupling it from resource consumption. Circular economy business models, such as leasing, allow full traceability of materials and enables the business to keep hold of its resources.”
As Ms. Gillen, LEED Process Manager at Emerald Skyline, noted in her February article, “Since construction and demolition waste constitutes one-third of all waste, it is necessary that the (commercial real estate) industry be methodically directed toward a circular economy, minimizing waste and maximizing value.
Emerald Skyline Corporation, whose principals include real estate, sustainability, resiliency, architecture and biological science professionals is uniquely qualified to advise you on how your organization can be a good corporate citizen and begin reaping the sustainable benefits of a circular economy. We can provide you with the tools and guidance you need to save money by being resourceful.
Remember the old adage “One person’s trash is another person’s treasure.” It’s time for us to realize, it is a treasure for all of us.
















